City: New York
Country / US State / US Territory: New York
Type of Solution: Seawalls and Living Shorelines
Climate Impact: Seal Level Rise; Hurricanes and Storm Surge; Extreme Precipitation and Flooding
Social Value Created: Educational and Career Development Opportunities; Active Living and Recreation; Community Engagement; Social Cohesion; Arts and Culture
Cost: $60 million
Funding Source: U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Rebuild by Design competition
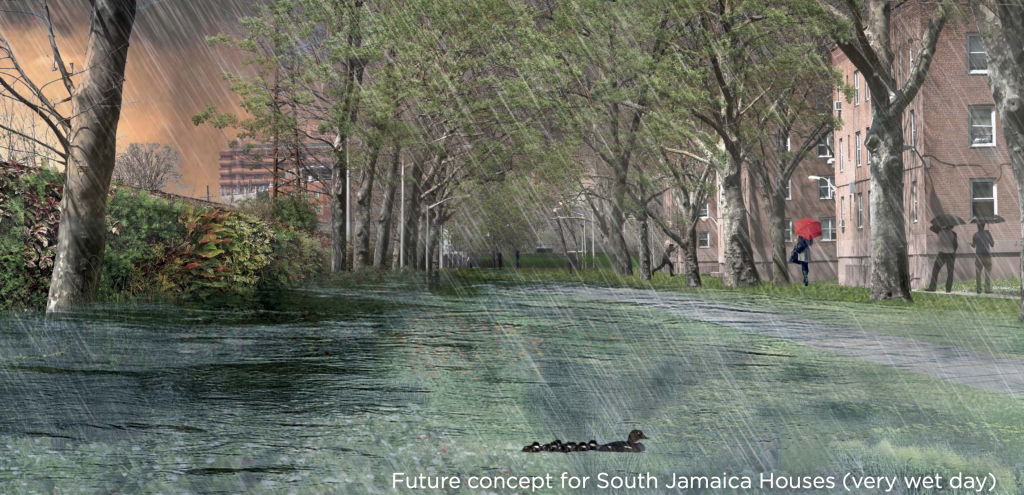
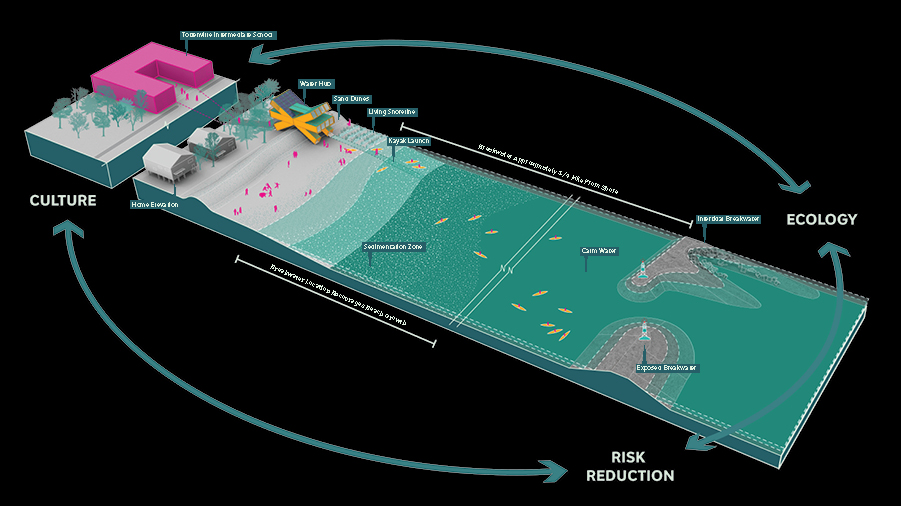
Living Breakwaters is a project aimed at helping to reduce wave energy, lowering flooding risks during extreme storm events. The project was developed by SCAPE landscape Architecture for the Rebuild Design Competition, a competition held by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) to improve coastal resilience in response to Hurricane Sandy.
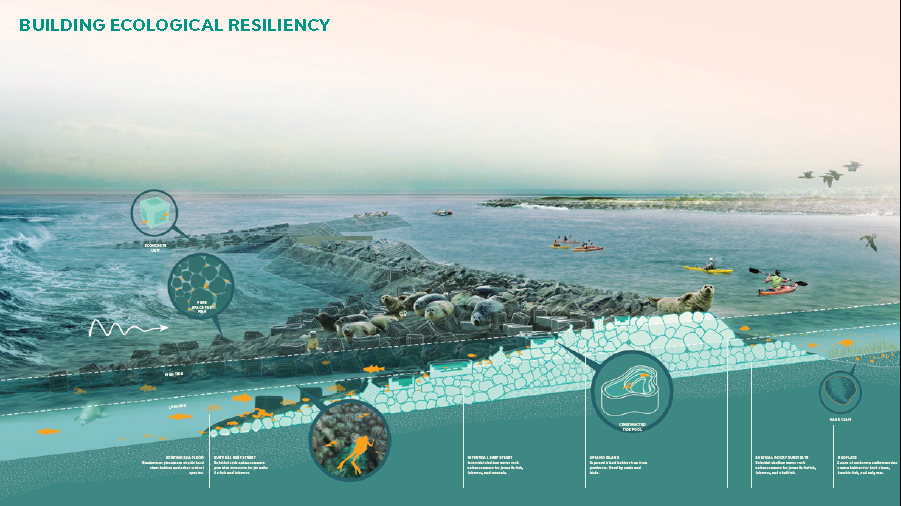
The Living Breakwaters approach uses structures to restore and enhance marine habitats, as well as improve biodiversity. Structures include reef ridges, reef streets, crenulated crests, and bio-enhancing concrete. This habitat mimics historic oyster reefs, which helps to restore the oyster population.
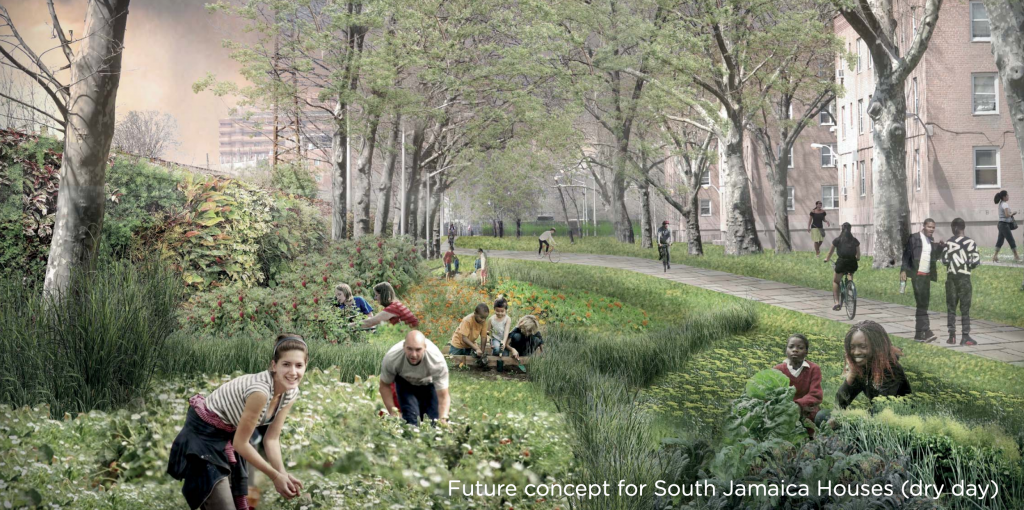
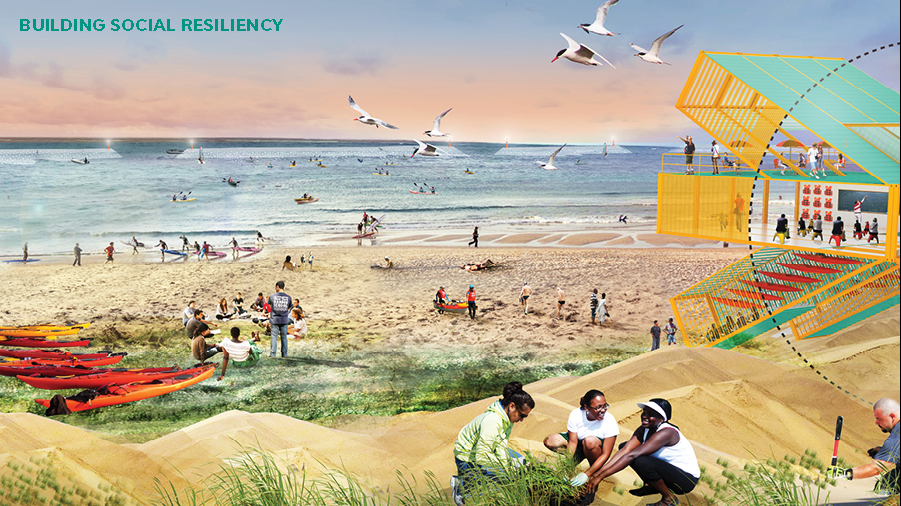
Additionally, the project co-creates social value. The project will help to prevent beach erosion and protect property values. The project also will improves access to the shoreline an recreational opportunities such as boating and fishing.
Also, an on-land Water Hub will be constructed on shore for visitoring groups, recreation, and educational programs. The Harbor School and Billion Oyster Project will create educational opportunities for local schools to learn about ecological stewardship and how they can help to protect Staten Island’s coastline. Implementation of the project also provides educational opportunities for research and skill development through project monitoring.

Sources
Atlas. (n.d.). Creating protective infrastructure to reduce coastal risk, enhance aquatic habitat, and foster social resilience. Retrieved from https://www.the-atlas.com/project?id=374#.
New York State. (n.d.). Learn more about the Living Breakwaters project. Retrieved from https://stormrecovery.ny.gov/learn-more-about-living-breakwaters-project.
Rebuild by Design. (n.d.). Living Breakwaters. Retrieved from http://www.rebuildbydesign.org/our-work/all-proposals/winning-projects/ny-living-breakwaters.