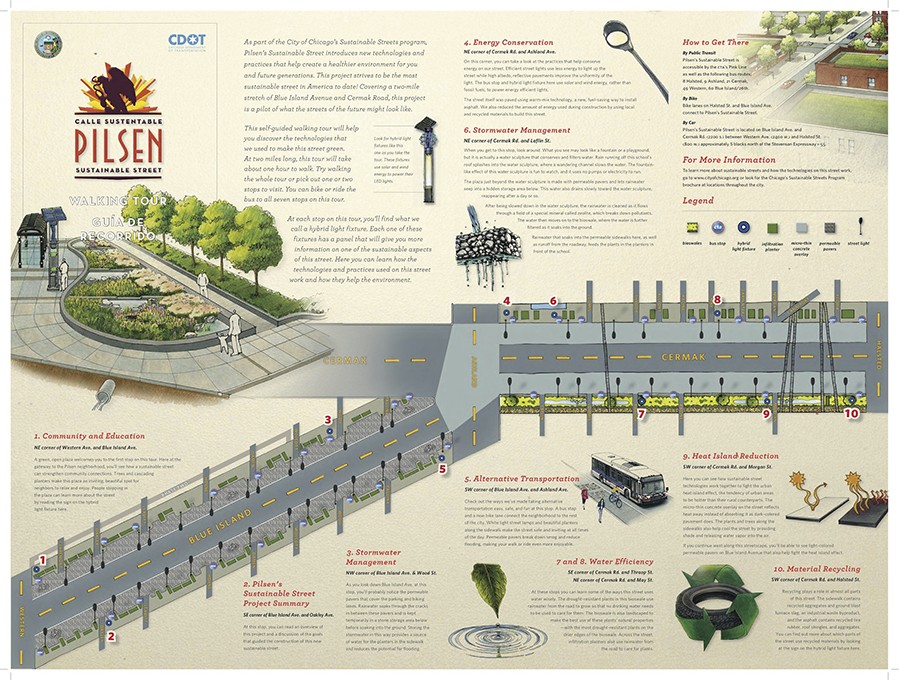
City: Miami
Country / US State / US Territory: Florida
Type of Solution: Habitat Restoration
Climate Impact: Seal level rise; Hurricanes and Storm Surge; Extreme Precipitation and Flooding
Social Value Created: Public Education; Community Engagement; Community Wellbeing and Quality of Life; Urban Beautification
Cost: $18.4 million
Funding Source: Public Space Challenge grant
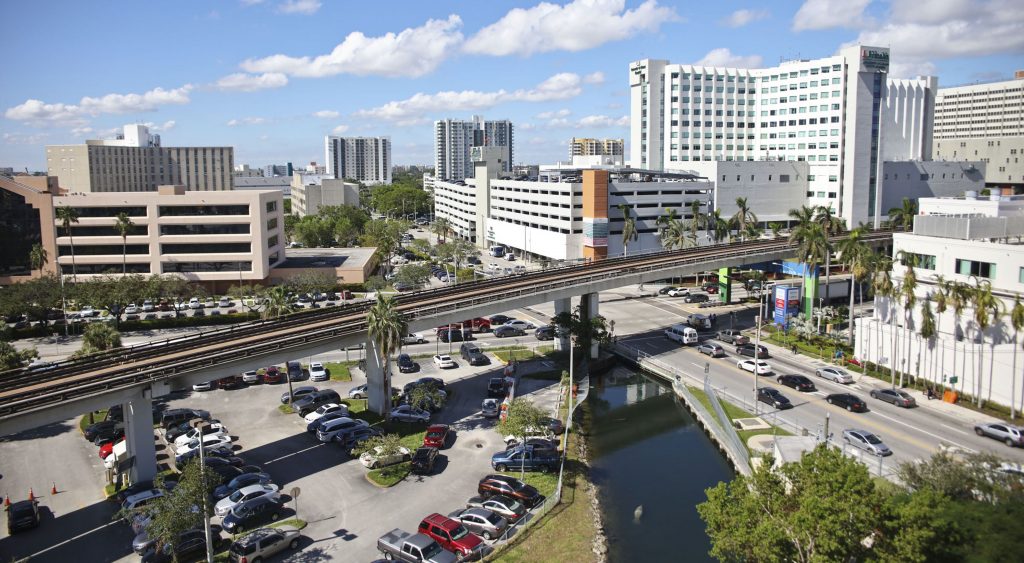
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) partnered with Greater Miami and the Beaches on a project to revitalize Wagner Creek. Over the years, Wagner Creek has been a site of illegal dumping, leaking pipe systems, and stormwater runoff from nearby auto-repair shops, making it one of the most polluted water bodies in Florida. The project will use green infrastructure improve stormwater management in response to flooding from heavy precipitation events and storm surge, as well as to remove pollutants and improve water quality.
Green infrastructure also provides shade, helping to cool the urban environment and mitigate extreme temperatures and the urban heat island effect. Additionally, the project aims to improve community well-being and contribute to urban beautification.
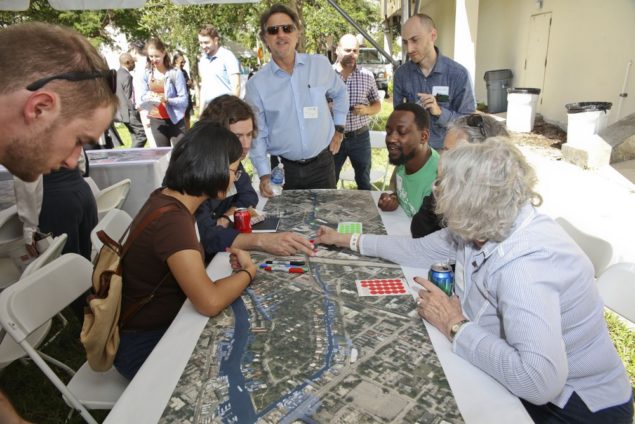
During the design phase of the project, TNC held a public visioning workshop that engaged stakeholders with various backgrounds. Stakeholders identified different services the project could provide and were given stickers to prioritize these services, such as larger/smaller parking lots, parks, tree plantings, and improve water quality for recreation. Then, the University of Miami Landscape Architecture department assisted with developing designs that could be implemented, incorporating climate change projections and other datasets, contributing to the advancement of education. A number of parks are planned as part of the project, and these parks will serve an estimated 100,000 people that live and work in the area.


Sources:
Heffernan, J. (November 25, 2017). The Nature Conservancy launches effort to revitalize the banks of Wagner Creek. Miami’s Community Newspapers. Retrieved from https://communitynewspapers.com/brickell/the-nature-conservancy-launches-effort-to-revitalize-the-banks-of-wagner-creek/.
The Nature Conservancy. (November 8, 2017). The Nature Conservancy to revitalize Wagner Creek. Retrieved from https://www.nature.org/ourinitiatives/regions/northamerica/unitedstates/florida/newsroom/florida-revitalizing-miamis-wagner-creek.xml.
The Nature Conservancy. (n.d.). The greening of Wagner Creek. Retrieved from https://www.nature.org/ourinitiatives/regions/northamerica/unitedstates/florida/explore/florida-wagner-creek-restoration.xml.
*Note: This case was documented from an interview with a city practitioner.