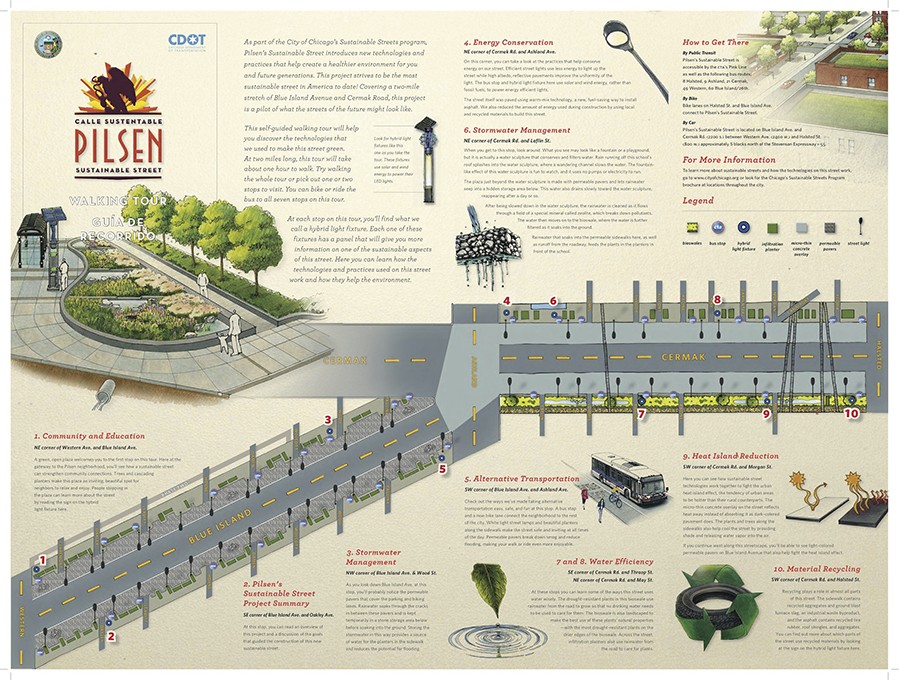
City: San Francisco
Country / US State / US Territory: California
Type of Solution: Habitat Restoration
Climate Impact: Seal Level Rise; Hurricanes and Storm Surge; Extreme Precipitation and Flooding
Social Value Created: Community Engagement; Employment Opportunities; Water Security and Quality; Property Values; Active Living and Recreation; Urban Beautification
San Francisco has set a goal to restore 100,000 acres of the bay’s tidal marshes. A 2015 study projects that most of the existing marshes will be damaged or destroyed by 2100. The City has identified restoration of marshes as a strategy for managing sea level rise, as it provides the community with other socially value co-benefits unlike other sea level rise solutions.
Through restoration initiatives and innovative strategies, marshes can be restored and enhanced to prepare for sea level rise and coastal flooding. Additionally, the marshes help to filter pollutants out of runoff to improve water quality, and they provide habitat for many at-risk species and species critical to the economy, such as Dungeness crab and salmon. Further, restoration projects help to control coastal erosion of water front properties.
Sonoma Land Trust acquired 1,000 acres of tidal marshes in the Sears Point Wetland along the northern shore of San Francisco Bay. For the project, 285 feet of an existing levee was breached to restore previous marsh land, creating a “habitat” levee using marsh mounds, or raise “islands”. 500 marsh mounds were constructed, each of which are 6 feet tall and 50-75 feet wide, using reclaimed sediment. These mounds support marsh accretion and provide cover for nesting birds from the rising tides and waves during storms. The “habitat” levee both protects the adjacent a nearby highway and railroad and provides additional wildlife habitat.
The project also includes the development of a 2.5 mile section of the Bay Trail, a recreational trail running through the marshes. This addition will provide users with views of Mt. Tamalpais, Mt. Diablo, and the San Francisco skyline, as well as include new benches, interpretive signs, and parking.
South Bay Salt Pond Restoration Project is another project underway, seeking to restore 15,100 acres of former commercial salt ponds to functional tidal marshes. The Project is will manage coastal flooding, as well as improve wildlife habitat and increase public recreational access. A 400 foot berm will be constructed to help control flooding. 16 islands, each 15,000 square feet, will also be constructed. Levees will also be lowered and breeched to restore 130 acres of tidal pools.
In addition to flooding control measures, public recreational trails will be realigned and resurfaced to improve public access, and two overlooks and four interpretive panels will be installed.
Environmental Protection Agency. (n.d.). South Bay Salt Pond Tidal Marsh Restoration at Pond A17 Project. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/sfbay-delta/south-bay-salt-pond-tidal-marsh-restoration-pond-a17-project.
Small-Lorenz, S. L., Stein, B. A., Schrass, K., Holstein, D. N., & Mehta, A. V. (2016). Natural defenses in action: harnessing nature to protect our communities. National Wildlife Foundation, Washington, D.C. Retrieved from https://www.nwf.org/~/media/PDFs/Global-Warming/Reports/NWF_Natural-Defenses-in-Action_Report.pdf.
Sonoma Land Trust. (June 6, 2014). Sonoma Land Trust and Ducks Unlimited kick off construction of Sears Point 960-Acre Wetland Restoration Project on San Pablo Bay. Retrieved from https://www.sonomalandtrust.org/news_room/press_releases/1406-sears-point.html.
Sonoma Land Trust. (n.d.). Seas Point Wetland Restoration Project groundbreaking FAQs. Retrieved from https://sonomalandtrust.org/news-room/jenner-information-kit/faq/.
South Bay Salt Pond Restoration Project. (n.d.). Project description. Retrieved from http://www.southbayrestoration.org/Project_Description.html.
Wood, J., Pitkin, M., Meisler, J., DiPietro, D., Graffis, A., & Fris, R. (January 17, 2018). Saving tidal marshes in the San Francisco Bay. U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit. Retrieved from https://toolkit.climate.gov/case-studies/saving-tidal-marshes-san-francisco-bay.